low flow low gradient aortic stenosis review
In this case low flow and subsequent low transvalvular gradient are present and this entity is referred to as LF-LG AS with low LVEF. Depending on the ejection fraction reduced vs.
Assessment Of Aortic Valve Disease A Clinician Oriented Review
A squared function of flow and may thus be pseudo-normalized and underestimate stenosis severity in presence of low flow.

. Severe aortic stenosis is defined by a mean gradient 30 mm Hg at any time during the dobutamine study provided the effective. Low flow is defined in the guidelines as a stroke volume index transvalvular pressure gradient is highly flow-dependent ie. We discuss current diagnostic and treatment modalities for low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis.
The term Low Flow Low Gradient remember velocitygradients are FLOW DEPENDENT. The occurrence of low-flow low-gradient severe aortic stenosis in patients with normal left ventricle LV ejection fraction has only been recently described. This entity is the so-called low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS.
This article summarizes current guidelines and best practices for the management of. This discordant echocardiographic data creates doubts about the severity of the disease. The severity of low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis cases continue to be misunderstood because of challenging diagnosis and treatment remains complex.
True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be di. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat. N 2007 we reported that a substantial proportion of patients with severe aortic stenosis may have alowflow lf ie reduced stroke volume and thus often have a low transvalvular pressure gradient lg despite a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction lvef1the2014americancol- lege of cardiology accamerican heart association.
Crossref Medline Google Scholar. In this review an approach to the clinical pathways for assessment of low flow low gradient aortic stenosis has been discussed. Recent findings In the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association guidelines the criteria for severe.
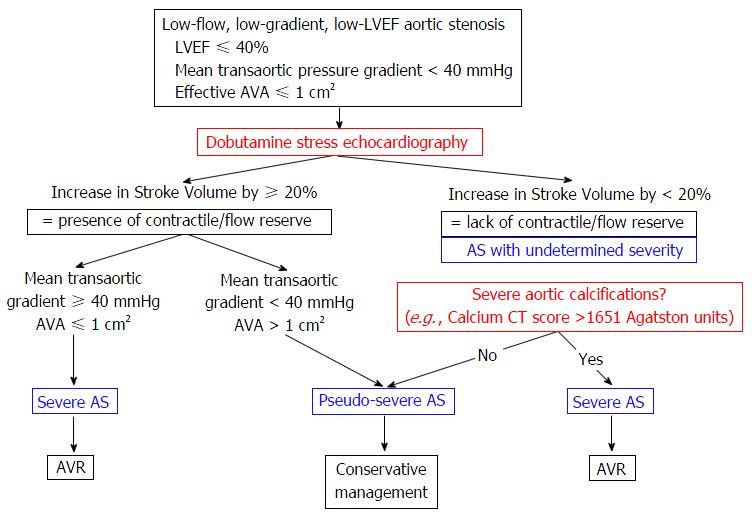
The diagnostic criteria are. Of patients with severe AS 30 to 50 present with low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS status. Low gradient low flow aortic stenosis is defined by a left ventricular ejection fraction 40 mean gradient 30 mm Hg and effective orifice area 10 cm 2.
Outcome after aortic valve replacement for low-flowlow-gradient aortic stenosis without contractile reserve on dobutamine stress echocardiography. Purpose of review. Paradoxical low-flow aortic valve stenosis is defined as the presence of small valve area cw severe Aortic stenosis low transvalvular gradients non -severe range in the presence of low transvalvular flow but with normal ejection fraction 50.
The indications of the guidelines recommend surgical or percutaneous treatment depending on the risk and. Dobutamine stress echocardiography is necessary. During the symptomatic stage the rate of death increases dramatically so that a precise diagnostic approach is taken to guide therapeutic options.
A squared function of flow and may thus be pseudo-normalized and underestimate stenosis severity in presence of low flow. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis is a highly challenging condition in terms of diagnosis and therapeutic management. Different Patterns of Flow Gradient Aortic Stenosis In the American Heart AssociationAmerican College of Cardiology and European Society of CardiologyEuropean Association of Cardiothoracic Surgery guidelines12 severe aortic stenosis AS is defined as a peak aortic jet velocity 40 ms a mean gradient 40 mm Hg or an aortic valve area AVA.
Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis with Low Ejection Fraction When ventricular systolic dysfunction is present the myocardium can not contract strongly enough to pump blood with a lot of pressure. Theless severe AS can be present in patients with low forward flow resulting in a peak valve velocity. Low-flow low-gradient LF-LG aortic stenosis with depressed left ventricular LV ejection fraction is a diagnostic challenge that is frequently.
Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis LFLG AS with reduced left ventricle ejection fraction LVEF is still a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. A subset of AS patients have low flow low mean gradients with preserved ejection fraction in whom one must evaluate global hemodynamic load to assess ventriculo-arterial impedence. The stroke volume is low 35 mLm² velocitygradients are low.
In both cases the decrease in gradient relative to AS severity is due to a reduction in transvalvular flow. Previous article Next article Keywords. In this review an approach to the clinical pathways for assessment of low flow low gradient aortic stenosis has been discussed.
J Am Coll Cardiol. Preserved will guide us to different questions. In this review an approach to the clinical pathways for assessment of low flow low gradient aortic stenosis has been discussed.
LFLGAS occurs in 30 to 50 of patients with severe AS5It shows an AVA. This pattern of low-flowlow-gradient aortic stenosis is relatively well known and accepted in AS patients with depressed LV function where it was assumed that the failing LV cannot generate a high-flowhigh-gradient across the stenotic valve. 1 to assess the presence of lv flow reserve fr and 2 to differentiate truesevere versus pseudosevere as.
Low flow is defined in the guidelines as a stroke volume index transvalvular pressure gradient is highly flow-dependent ie. A subset of AS patients have low flow low mean gradients with preserved ejection fraction in whom one must evaluate global hemodynamic load to assess ventriculo-arterial impedence. Low-flow low-gradient LF-LG aortic stenosis AS may occur with depressed or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF and both situations are among the most challenging encountered in patients with valvular heart disease.
In a low flow state the gradient may be pseudo-normalized and thus underestimate the stenosis severity whereas the AVA may be pseudo-severe and thus overestimate the severity. Aortic stenosis AS is the most frequently observed valvular heart disease. However these patients continue to have a.
A subset of AS patients have low flow low mean gradients with preserved ejection fraction in whom one must evaluate global hemodynamic load to assess ventriculo-arterial impedence. The surgical mortality for patients with classic low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis CLFLG AS has decreased in recent decades. 2014 ACCAHA Guidelines Recommendations for AVR in Patients with LF-LG AS.
The purpose of this review is to highlight the diagnostic and management specificities of this entity. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit. The aim of this paper is to review the latest evidences about the assessment of the valvular disease usually difficult because of the low-flow status and the therapeutic options.

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Algorithm For The Diagnostic Workup And Management Of Normal Flow Download Scientific Diagram

Subtypes Of Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis As Aortic Stenosis Ava Download Scientific Diagram

Evaluation And Management Of The Patient With Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Imaging Strategies For Evaluating Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis With Reduced And Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Semantic Scholar

What Is New For General Cardiologists In The 2017 Esc Guidelines On Valvular Heart Disease

Distinction Of Classical And Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Case Of Classical Low Flow Low Gradient As With Pseudo Severe Stenosis Download Scientific Diagram
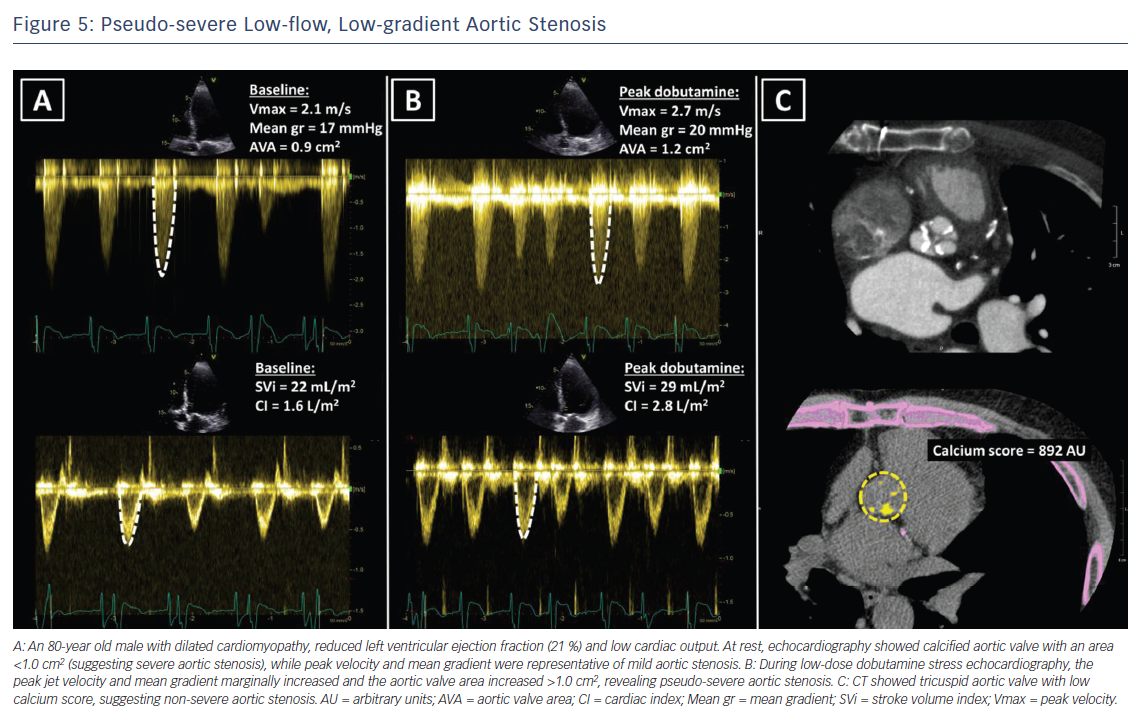
Figure 5 Pseudo Severe Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Aer Journal

Figure Stepwise Approach To The Complex Subgroup Of Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Evaluation Of Patients With Classical Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Download Scientific Diagram

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Distinct Disease Entity Heart

Prognosis Of Severe Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis By Stroke Volume Index And Transvalvular Flow Rate Jacc Cardiovascular Imaging

Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography In Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Flow Reserve Does Not Matter Anymore

Simplifying The Approach To Classical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Renewed Emphasis On The Resting Transthoracic Echocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology

Complex Scenarios Paradoxical Low Gradient As In Normal Patients
